Experiment Title: Open Circuit Test of a 3-Phase Alternator
1.
Objective
- Understand the behavior of an alternator under no-load
conditions.
- Calculate the synchronous reactance and field current
required for excitation.
2.
Apparatus
The following equipment was used
during the experiment:
- 3-phase alternator (synchronous generator)
- AC power supply
- Ammeter and voltmeter
- Rheostat (for field current control)
- Tachometer (to measure rotor speed)
- Circuit breaker and safety switches
3.
Theory
3.1
Open Circuit Test
The open circuit test (also known as
the no-load test) is conducted to determine the following parameters:
- Synchronous reactance ((X_s)): The impedance seen by
the alternator when no load is connected.
- Field current ((I_f)): The current required to establish
the magnetic field in the rotor.
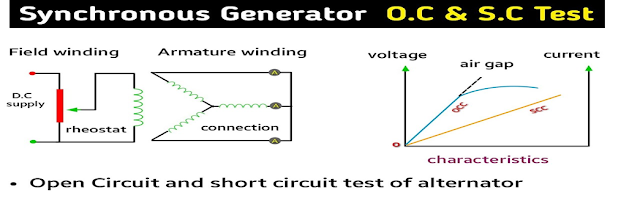
A three-phase alternator, also known as a
synchronous generator, converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The
open circuit test, also called the no-load test, involves running the
alternator at its rated speed without connecting any external load. During this
test, the field current is varied, and the corresponding terminal voltage is
measured to plot the open circuit characteristics (OCC).
4.
Circuit Diagram
5.
Procedure
- Connect the alternator to the AC power supply.
- Open the circuit breaker to disconnect the load.
- Gradually increase the field current using the
rheostat.
- Measure the line voltage ((V_{\text{line}})) and field
current ((I_f)).
- Record the rotor speed using the tachometer.
- Calculate the synchronous reactance: [ X_s =
\frac{{V_{\text{line}}}}{{I_f}} ]
- Determine the synchronous speed ((N_s)) based on the
number of poles: [ N_s = \frac{{120 \cdot f}}{{P}} ]
- Compare the measured rotor speed with the synchronous
speed.
6.
Discussion
Discuss the results obtained during
the experiment:
- Plot the synchronous reactance curve (reactance vs.
field current).
- Analyze any deviations from ideal behavior.
- Consider factors affecting the alternator’s
performance.
7.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the open circuit test
provides valuable information about the alternator’s characteristics. We
learned about synchronous reactance, field current, and the importance of
no-load testing. Understanding these parameters helps in designing and
operating synchronous generators effectively.