Everything You Need to Know About 3-Phase Induction Motors
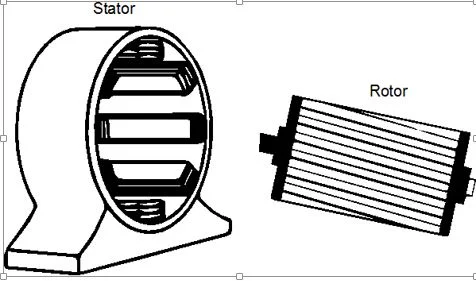
Stator
ü Stator carries a 3-Φ winding (Stator Winding) which is fed from 3-Φ supply
ü Slots are provided on the inner periphery of the stator which houses the 3 phase winding.
ü When 3-phase supply is given to the stator winding, a rotating magnetic field (RMF) of constant magnitude is produced.
ü This
RMF induces currents in the rotor by electromagnetic induction due to RMF.
Rotor
v Rotor carries a short-circuited winding known as rotor winding which receives power from stator
by electromagnetic induction.
Ø 2 types of rotor
1. 1 . Squirrel cage type
2. Wound type
Squirrel cage type rotor













good job.
ReplyDelete